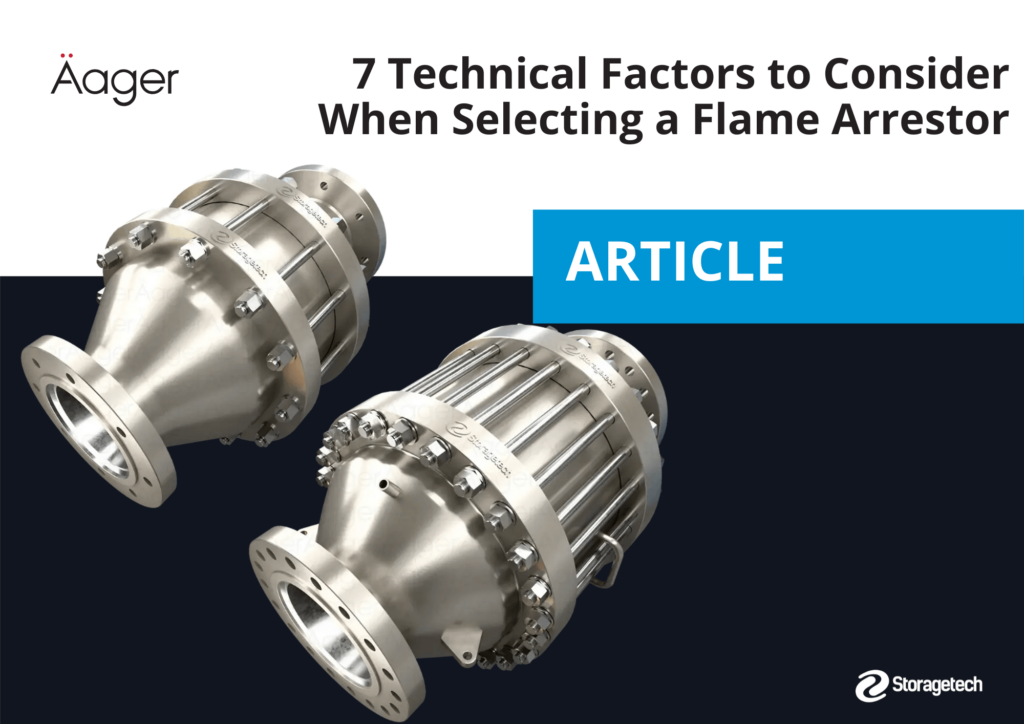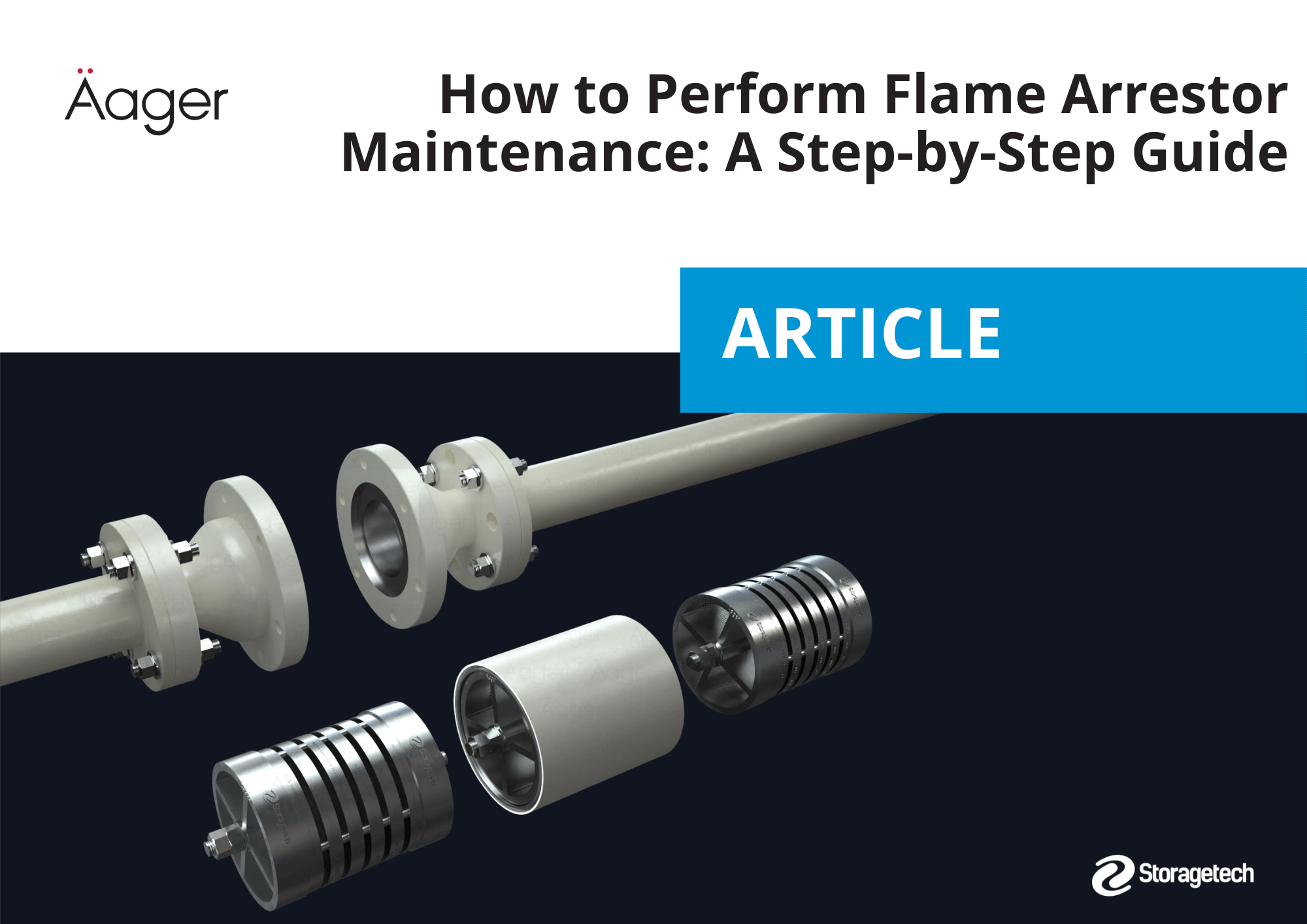
Flame arrestors play a critical role in preventing the spread of flames in environments where flammable or explosive gases are present. For these devices to function safely and effectively, they require periodic maintenance and cleaning. Below is a step-by-step guide to help you perform flame arrestor maintenance and ensure optimal performance over the long term.
1. Establish a Maintenance Plan
a) Set a Regular Schedule
- Determine inspection intervals based on factors such as operating conditions, gas type, pressure, and temperature.
- Example: Monthly, quarterly, or semiannual routine checks, with a more comprehensive inspection once a year.
b) Prepare Spare Parts and Tools
- Obtain any replacement parts (seals, gaskets, mesh components, etc.) ahead of time.
- Have the necessary tools, cleaning agents, and personal protective equipment (PPE)—such as helmets, goggles, and gloves—ready for use.
Tip:
Align your plan with recommendations from standards like API or NFPA, as well as the flame arrestor manufacturer. Document and share the plan with the relevant maintenance teams.
2. Secure the System
a) Isolate the Line and the Device
- First, shut down or isolate the pipeline or tank where the flame arrestor is installed. Confirm it is no longer pressurized.
- If needed, close valves or halt the process flow entirely to ensure no gas is passing through the line.
b) Depressurize and Vent
- Release any residual pressure from the line or equipment and allow any remaining gases to vent safely.
- Provide adequate ventilation in the work area to prevent the accumulation of explosive gases.
Tip:
Follow Lockout/Tagout procedures during this step to prevent unauthorized access or accidental re-pressurization.
3. Remove the Flame Arrestor
a) Check the Connections
- Carefully loosen flange bolts, gaskets, and any other connections.
- Inspect gaskets during removal; any that are worn or damaged must be replaced.
b) Lift the Device Safely
- Use a hoist or other appropriate lifting equipment if the flame arrestor is heavy.
- Avoid causing dents or deformation on metallic surfaces during removal.
Tip:
Take notes or photos of the original orientation and assembly sequence to simplify reinstallation.
4. Perform Internal Inspection and Cleaning
a) Initial Visual Check
- Inspect the interior for burn residue, carbon deposits, rust, or corrosion.
- Look closely at the plates, mesh, or honeycomb structures for any signs of bending, tearing, or blockage.
b) Mechanical Cleaning
- If you find deposits or blockages, remove them with a suitable brush or compressed air.
- Use soft metal or plastic brushes for stubborn deposits to avoid damaging the metal surfaces.
c) Chemical Cleaning
- If mechanical cleaning is insufficient, use manufacturer-approved chemical cleaners. You can apply them by soaking parts or using cleaning baths.
- Always wear appropriate PPE (eye protection, gloves, respirator, etc.) when handling chemicals.
Tip:
After cleaning, dry all components with compressed air or a clean cloth. Moisture left behind can lead to rust or corrosion.
5. Check for Damage and Wear
a) Plates / Mesh Structure
- Inspect for thinning, holes, or other structural compromises that could reduce the flame arrestor’s ability to quench a flame.
- Bent or deformed parts should be replaced to maintain functionality.
b) Gaskets and Seals
- Gaskets must remain flexible to ensure a tight seal. Any that are cracked or hardened must be replaced.
- Inspect all seal surfaces (flange faces, etc.) for cracks or irregularities, and repair or replace as necessary.
c) Housing and Connection Points
- Look for corrosion, cracks, or deformation on the flame arrestor body.
- If the threads on bolts or other fasteners are worn, replace them to maintain a secure and leak-free connection.
Tip:
Record any damage or wear you detect and consult with the maintenance team or the manufacturer to confirm that replacement parts meet original certification requirements.
6. Reassemble and Reinstall
a) Reassemble in the Correct Order
- Reinstall cleaned and inspected components according to their original positions and orientations.
- Pay extra attention to the direction of plates or mesh; reversed installation can degrade performance.
b) Replace Seals and Gaskets
- Always use new gaskets to ensure a tight seal. Clean the flange faces before placing the new gaskets.
- Tighten bolts gradually and evenly, following the torque values recommended by the manufacturer.
c) Confirm Position and Flow Direction
- Most flame arrestors have an arrow indicating the flow direction. Ensure it matches your process setup.
- Make sure end-of-line or in-line models are installed in the correct orientation per manufacturer guidelines.
Tip:
After reassembly, perform a leak test at low pressure to check for any potential sealing issues.
7. Final Checks and Bringing the System Back Online
a) Pressure and Functional Testing
- Gradually restore operating pressure to the system and monitor the flame arrestor for unusual noise, vibration, or excessive pressure drop.
- Use the manufacturer’s testing protocols, if available, to ensure internal parts are properly seated and leak-free.
b) Resume Normal Operating Conditions
- Once gas flow is restored, observe the flame arrestor under standard pressure, temperature, and flow conditions for a short period.
- Immediately halt the process if you detect any anomalies (unexpected vibrations, pressure fluctuations, or strange sounds).
c) Documentation
- Record all findings, replaced parts, and test results in a maintenance log.
- These records will help you track equipment health, forecast future repairs, and demonstrate compliance with relevant standards.
Tip:
Maintain both digital and physical copies of maintenance records for easy retrieval and regulatory reporting.
Key Takeaways
Regular maintenance is crucial for ensuring that flame arrestors continue to perform at peak effectiveness. By consistently cleaning, inspecting for damage, and reassembling correctly, you preserve both safety and operational efficiency.
Follow this step-by-step guide to:
- Make the system safe and isolated before beginning.
- Remove and clean the flame arrestor’s internal components.
- Evaluate wear and damage, replacing any compromised parts.
- Reinstall the device with correct orientation and sealing methods.
- Log every maintenance activity to support compliance with industry standards and manufacturer recommendations.
Adhering to these steps will help keep your flame arrestors in top condition, providing reliable protection against the risk of flame propagation for years to come.

Mohammed HASSAN
Technical Coordinator