Please Click for Reading the Full Text in PDF Format here: Tank Storage Magazine Article — Choosing The Right Tank Cover

Dubai, January, 2023 — Äager GmbH’s VP of Sales & Marketing Mr. Rıza Altunergil participated in reportage from Tank Storage Magazine which was about choosing the right rank cover.
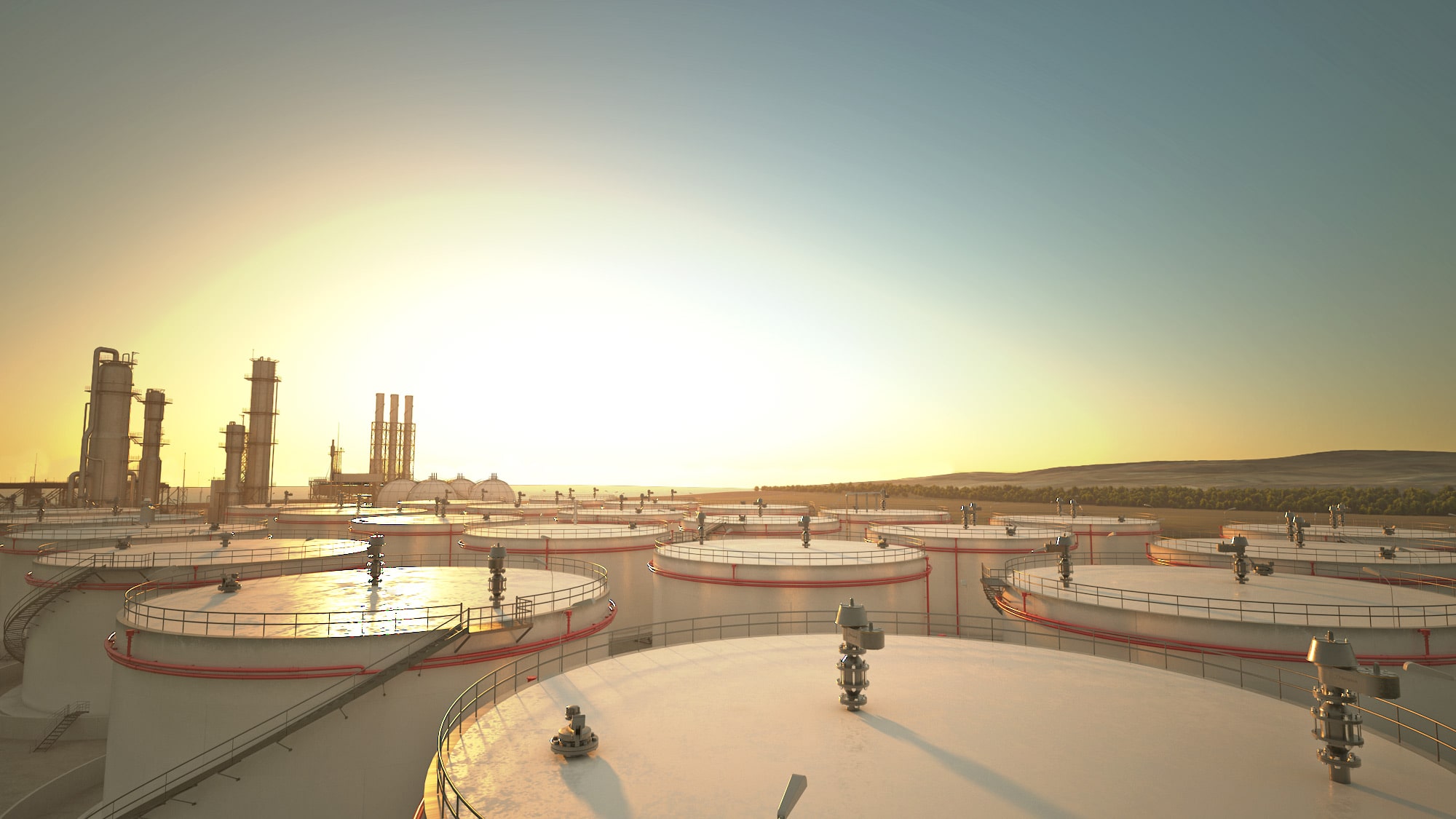
He mentioned that ‘There is no single solution for tank roofs. There are different types of roofs, such as conventional steel roofs, external floating roof, and dome roof, that are chosen for various parameters.’ One of those factors can be the risk of the product being stored. Each product has its own chemical characteristics and that causes certain chemical reactions with the roof material. For instance, we recommend stainless steel or special alloys for highly corrosive chemicals.»
Questions during interview?
Why is it crucial for there to be different tank roofs on the market?
There is not a single solution for tank roofs. There are different types of roofs; such as conventional steel roofs, external floating roof and dome roof, that are chosen for various parameters. We design tank roofs as per storage tank technical requirement, which are specified by industrial standards, however project budget, time and location also play an important role.
Can you explain the difference between a tank roof and a dome?
Main difference between a conventional steel tank roof and an aluminum dome roof is the material type. There is no doubt that aluminum is lighter than steel, needs very less maintenance, faster and safer to install and long lasting.
Why are steel and aluminium the optimum materials for roofs/domes?
There are obvious advantages to each material. Aluminum is used for dome roofs for its durability, long lasting, and light weight characteristics, however aluminum structures are not preferable for pressurized tanks. Carbon or stainless steel are on the other hand very common and easier to fabricate.
From your opinion, do you see any trends or patterns in which tank roof/dome is the most popular?
Particularly for chemical and hydrocarbon storage tanks, a new trend is using an internal floating roof with a dome roof. For water and wastewater industries, we see more and more storage tanks are built with aluminum dome roofs.
Does the roof/dome chosen depend on the product being stored?
Each product has its own chemical characteristics and that causes certain chemical reactions with the roof material. For instance; we recommend stainless steel or special alloys for highly corrosive chemicals.
Does a tank roof/dome chosen, change depending on the country (I.e because of different regulations, climate conditions etc)?
Yes, regional regulations and rules are clearly the main factor to choose the roof type. For instance, it is mandatory to use internal floating roofs in the majority of the world due to safety and environmental reasons, however weather conditions, and seismic zones are also other major factors that affect the roof design. Moreover, there are also special cases, too. For instance; we built a special underground bulk tank with carbon steel roof covered with concrete second layer in order to protect the tank against terrorist attacks.
What are the regulations surrounding tank roofs and domes?
We are following Directive 94/63 CE in Europe and EPA in the U.S.A. Similarly each region has pretty much similar regulations. It is highly appreciated that even countries like Nigeria, Pakistan, Cuba have their own regulations for storage tank roofs.
How can a tank roof/dome be made sustainable?
In case of hydrocarbons and chemicals, vapor loss, and emission control are the main factors. A tank with a high emission can lead to high effect on environment, human life and causes economical loss. Whether it is with an internal or external roof, choosing the right tank roof and equipment are highly important.
Why are tank roofs/domes often constructed separately from the rest of the tank?
Thanks to its lightweight and easy installation methods, contractors preferes to assemble the aluminum dome roofs on ground separately and lift it up for installation. This technique helps constructors to assemble the roof faster, with less labor and without need of a heavy crane.